In this tutorial, we will learn about how to sort ArrayList in Java. We will also learn how to sort an ArrayList in ascending order and descending order.
RELATED POST: How to Move All Zeroes Present in an Array to the End in Java?
What is an ArrayList?
An ArrayList is a class in Java that implements the List interface. It’s based on an Array data structure and is widely used for its functionality and flexibility. Developers often prefer ArrayList them over regular arrays because they can dynamically grow and shrink as elements are added or removed. This eliminates the need for manual size management.
An ArrayList is a dynamic, resizable implementation of the List interface in Java. It is part of the java.util package and provides a flexible way to store and manipulate collections of elements.
Unlike arrays, ArrayList automatically grows and shrinks as elements are added or removed, eliminating the need to manually manage the size. It offers various methods to add, remove, access, and manipulate elements.
One advantage of using ArrayList is that it allows the storage of objects of any type, including both primitive types (int, char, etc.) and reference types (String, Object, etc.).
How to Create an ArrayList in Java
- Create a
ArrayListwith duplicate elements. - Create a new
HashSetobject, which is a collection that does not allow duplicates. - Add all the elements from the
ArrayListto theHashSet. SinceHashSetdoes not allow duplicates, it will automatically remove them. - Create a new
ArrayListand add all the elements from theHashSetback to the newArrayList. - Now, the new
ArrayListwill contain unique elements.
Example :
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class ArrayListUniqueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
// Add duplicate elements to the ArrayList
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(2);
numbers.add(9);
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(2);
// Create a HashSet and add all elements from the ArrayList
HashSet<Integer> uniqueSet = new HashSet<>(numbers);
// Create a new ArrayList and add all elements from the HashSet
ArrayList<Integer> uniqueNumbers = new ArrayList<>(uniqueSet);
// Print the ArrayList
System.out.println("Unique ArrayList: " + uniqueNumbers);
}
}Output :
Unique ArrayList: [2, 5, 9]In this example, we start with a ArrayList called numbers that contains duplicate elements. We create a HashSet called uniqueSet and pass the numbers list to its constructor. The HashSet automatically removes duplicates while retaining the order of the elements.
Next, we create a new ArrayList called uniqueNumbers and pass the uniqueSet to its constructor. This creates a new ArrayList containing only unique elements. Finally, we print the unique ArrayList.
Check out My Latest post on Developer Helps for some Interesting Insights
↠ What is the Cannot find symbol Error in Java?
↠ How to Find the Size or Length of an Array in JAVA?
↠ How to Copy an Array in JAVA?
↠ How to Move All Zeroes Present in an Array to the End in Java?
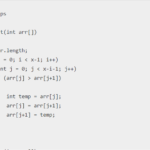
Sort an Arraylist in Ascending Order
To sort ArrayList in ascending order in Java, you can use the Collections class from the Java standard library. The Collections class provides a sort() method that can be used for this purpose. Here’s an example that demonstrates how to sort ArrayList in ascending order:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class ArrayListSortingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements to the ArrayList
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(2);
numbers.add(9);
numbers.add(1);
// Sort the ArrayList in ascending order
Collections.sort(numbers);
// Print the sorted ArrayList
System.out.println("Sorted ArrayList in ascending order: " + numbers);
}
}Output :
Sorted ArrayList in ascending order: [1, 2, 5, 9]In this example, we create a ArrayList called numbers and add some integers to it. Then, we use the Collections.sort() method to sort the numbers list in ascending order. Finally, we print the sorted ArrayList.
By utilizing the Collections.sort() method, you can easily sort an ArrayList in ascending order, as shown in the given example
Sort an ArrayList in Descending Order
To sort an ArrayList in descending order in Java, you can use the Collections class provided by the Java standard library. The Collections class offers a static method called sort() that can be used to sort a list in ascending order. However, to do a descending order, you need to use a custom comparator. Here’s an example of how to sort an ArrayList in descending order:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArrayListDescendingSortingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
// Add elements to the ArrayList
numbers.add(5);
numbers.add(2);
numbers.add(9);
numbers.add(1);
// Sort the ArrayList in descending order
Collections.sort(numbers, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer num1, Integer num2) {
return num2.compareTo(num1);
}
});
// Print the sorted ArrayList
System.out.println("Sorted ArrayList in descending order: " + numbers);
}
}Output :
Sorted ArrayList in descending order: [9, 5, 2, 1]In this example, we create an ArrayList called numbers and add some integers to it. To sort the ArrayList in descending order, we use the Collections.sort() method and pass a custom Comparator object as the second argument. Inside the compare() method of the Comparator, we compare the elements in reverse order by using num2.compareTo(num1) instead of the usual num1.compareTo(num2).
Finally, we print the sorted ArrayList in descending order.