In this Tutorial, we will learn about polymorphism in Java.
So the first question arises i.e. what is polymorphism in java and how it works. Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on many forms. The most common use of polymorphism in OOP occurs when a parent class reference is used to refer to a child class object. Any Java object that can pass more than one IS-A test is considered to be polymorphic. In Java, all Java objects are polymorphic since any object will pass the IS-A test for their own type and for the class Object
Polymorphism is a process in java by which we can use a method in multiple ways or polymorphism to make the method take different forms in java. The child class takes its reference from the parent class. This process is performed either by overloading in java or overriding in java. We use polymorphism when we aim at building an interface with different objects but the same form.
When we create a new object in the program, it takes the form of previous or inherited objects of the parent class via polymorphism. So we can perform many functions in various ways. Just like an animal can have various characteristics at a time. A leopard can be orange in color, ferocious in nature, and striped. As a result, he is so many things at the same time, so this is an example of polymorphism.
Here are some very useful features that we can use polymorphism in Java for:
- It allows the coder to reuse the classes, methods and code again and again.
- We can perform a single function more than one time.
- Even the data types such as int, float, long, double etc. can be used multiple times.
- Simply design one interface and use its objects as many times as you want.
- It allows us to create a code which remains consistent.
Example :
A superclass named “Shapes” has a method called “area()”. Subclasses of “Shapes” can be “Triangle”, “circle”, “Rectangle”, etc. Each subclass has its way of calculating area. Using Inheritance and Polymorphism means, the subclasses can use the “area()” method to find the area’s formula for that shape.
class Shapes {
public void area() {
System.out.println("The formula for area of a shape is not defined.");
}
}
class Triangle extends Shapes {
public void area() {
System.out.println("Triangle area = 0.5 * base * height");
}
}
class Circle extends Shapes {
public void area() {
System.out.println("Circle area = 3.14 * radius * radius");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shapes myShape = new Shapes(); // Create a Shapes object
Triangle myTriangle = new Triangle(); // Create a Triangle object
Circle myCircle = new Circle(); // Create a Circle object
myShape.area();
myTriangle.area();
myCircle.area();
}
}
Output :
The formula for area of a shape is not defined.
Triangle area = 0.5 * base * height
Circle area = 3.14 * radius * radiusTypes of Polymorphism in Java
Polymorphism in Java can be achieved in two ways i.e., method overloading and method overriding.
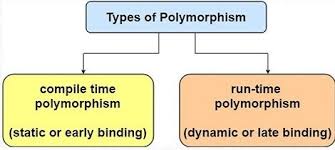
Polymorphism in Java is mainly divided into two types.
- Compile-time polymorphism
- Runtime polymorphism
Compile-time polymorphism can be achieved by method overloading, and Runtime polymorphism can be achieved by method overriding.
Run time polymorphism: A process It is a process in which a call made to an overridden function is settled at runtime. Dynamic method dispatch is the synonym for run time polymorphism. Below is an example to understand run time polymorphism.
Runtime polymorphism is also called Dynamic method dispatch. Instead of resolving the overridden method at compile-time, it is resolved at runtime.
Here, an overridden child class method is called through its parent’s reference. Then the method is evoked according to the type of object. In runtime, JVM figures out the object type and the method belonging to that object.
Runtime polymorphism in Java occurs when we have two or more classes, and all are interrelated through inheritance. To achieve runtime polymorphism, we must build an “IS-A” relationship between classes and override a method.
Method overriding
If a child class has a method as its parent class, it is called method overriding.
If the derived class has a specific implementation of the method that has been declared in its parent class is known as method overriding.
class Tree {
void Print()
{
System.out.println("Roots are the parents of the tree");
}
}
class Plant extends Tree {
void Print()
{
System.out.println("Plants are green");
}
}
class Leaves extends Tree {
void Print()
{
System.out.println("Leaves are fresh");
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Tree t;
t = new Plant();
t.Print();
t = new Leaves();
t.Print();
}
} The output of this program will be:
Plant
LeavesSo the child classes- plant and leaves will inherit all the features of parent class Root.
Compile-time polymorphism: This type of polymorphism is either achieved by method overloading or operator overloading. Static polymorphism is the synonym for compile-time polymorphism. In this, we can have multiple methods with the same name even if the methods have different parameters, sequences, or data types.
This type of polymorphism in Java is also called static polymorphism or static method dispatch. It can be achieved by method overloading. In this process, an overloaded method is resolved at compile time rather than resolving at runtime.
Method overloading
Consider a class where multiple methods have the same name. It will be difficult for the compiler to distinguish between every method.
To overcome this problem, we pass a different number of arguments to the method or different types of arguments to the method. In this way, we achieve method overloading.
In other words, a class can have multiple methods of the same name, and each method can be differentiated either by bypassing different types of parameters or bypassing a different number of parameters
Below is an example of method overloading while performing Polymorphism in java:
class Addnumbers{
static int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
static double Add(double x, double y)
{
return x + y;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(Addnumbers.Add(10, 20));
System.out.println(Addnumbers.Add (20.5, 30.3));
}
}
The output of this program will be:
30
50.8Now, we will discuss an example of operator overloading in java
class Operator {
void operator(String x, String y)
{
String str = x + y;
System.out.println("The final string will be - "
+ str);
}
void operator(int a, int b)
{
int c = a + b;
System.out.println("Sum = " + c);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Operator obj = new Operator();
obj.operator(100, 200);
obj.operator("Hello", "Sir");
}
} The output of the program will be:
300
The final string will be – HelloSirHence polymorphism is an object-oriented language concept simple meaning taking more than one form. As the main difference between overloading and overriding in polymorphism is that overriding is done inside different classes whereas overloading is done inside the same class. An object which passes two IS-A relationship test is always polymorphic in nature- one for itself and one for the object class.
Polymorphism and Inheritance
Polymorphism occurs when there is inheritance, i.e., many classes are related to each other.
Inheritance is a powerful feature in Java. Java Inheritance lets one class acquire the properties and attributes of another class. Polymorphism in Java allows us to use these inherited properties to perform different tasks. Thus, allowing us to achieve the same action in many different ways.