When a python pass statement is executed, basically what happens is nothing. This statement is simply used to execute a block of code in proper syntax without any commands. So pass statement in python is basically null. The result is also null with no output or operational values inside it. It can also be used as a placeholder in the program. In the code, a comment can be ignored but a pass statement cannot be ignored.
For example, as a user I want to execute a code but not at that point of time. May be in future I would want to execute that particular code. Since, it cannot have an empty body, so in that case the compiler might give an error or throw an exception. There comes the use of ‘pass’ when a body is constructed without any use and it contains nothing.
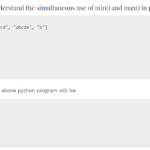
Below is a very simple illustration of a python program which shows the use of ‘pass’:
for letter in 'DeveloperHelps':
if letter == 'h':
pass
print 'This is a pass block'
print ('Current Letter is =', letter)
print "Thankyou!"The output of this python program will be:
Current Letter is = D
Current Letter is = e
Current Letter is = v
Current Letter is = e
Current Letter is = l
Current Letter is = o
Current Letter is = p
Current Letter is = e
Current Letter is = r
Current Letter is = H
Current Letter is = e
Current Letter is = l
Current Letter is = p
Current Letter is = s
Thankyou!
Check out My Latest post on Developer Helps for some Interesting Insights
↠ What do you mean by Python Enum?
↠ How to Convert Kilometers to Miles in Python?
↠ How to Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit in Python?
There can be other cases as well. Suppose we have a list and the user wants to delete all the odd numbers from that list. For this, the user has to make the use of loop to traverse all the numbers and sort the odd numbers from that list. The logic behind this will be: if the number will be divisible by two, it is even; otherwise it will be removed being odd. Hence, the list will return only even numbers which are divisible by two as the output. In that case, if there is a use of temporary list for the numbers, python won’t support it. The user needs to use ‘pass’ to execute no-operation statement. Or it will simply by pass the code which is not being used.
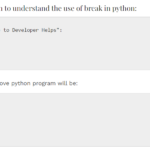
Below is python code to see what happens if an empty code is run without pass statement:
def Help():
# TODO - implement laterThis will throw an error saying “IndentationError: expected an indented block” as the output.
Can we have multiple pass Statement in the same program?
Yes, a python program can have multiple pass statements in a block. The reason lying behind this is a pass statement never terminates the function call. Its only role is to provide an empty block which can be of use in the future.
Python Pass Statement Example
def DeveloperHelps():
pass
print('Hello')
pass
if True:
pass
pass
print('True')
else:
print('False')
pass
pass
The output of the above python program will be:
TruePython pass Vs continue
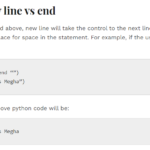
When the user uses ‘continue’ keyword, it means he wishes to start the execution of the loop inside the code in the next iteration. However, the use of pass is for an empty block. There is no compulsion for the block to execute. ‘continue’ always goes back to the top of the loop however ‘pass’ keeps moving on with the code flow during the processing.
Python pass vs return
A return statement in python will simply let the user exit the function in operation and return the output. For example, if the user wants to calculate the sum of two numbers. He can simple write return a+b and get the output. However, as we have learnt about pass keyword, it would not return any output. it is carried along in the code for syntactic results majorly.