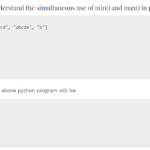
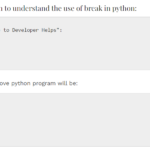
Python modules & packages play a very important role while working on a code. A module in python is basically a file containing the Python code. However, a package can be defined as a directory that holds sub-packages and modules. A package must hold the file __init__.py. This does not apply to modules. To import everything from a module, we always use *
Python Modules
A file containing a set of functions you want to include in your application is called python modules.
Creating a Module
To create a module, the user just has to save the code you want in a file with the file extension .py
def company(name):
print("Hello, " + name)Using a Module
The user can use the modules which he creates by using the import statement:
import mymodule
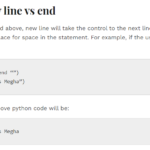
mymodule.company("Megha")Naming a Module
The user can name the module file whatever he likes, but it must have the file extension .py
import mymodule as mx
a = mx.person1["age"]
print(a)Built-in Modules
There are several built-in modules in Python which user can import whenever he likes.
import platform
x = platform.system()
print(x)Python Packages
A Python package usually consists of several modules. A package folder usually contains one file named __init__.py that basically tells Python: “Hey, this is a package!” The init file may be empty, or it may contain code to be executed upon package initialization.
Importing directory from package
We can import modules from packages using the dot (.) operator.
For example, if we want to import the start module in the above example, it is as follows:
import company.joblevel.startWe can now call the function simply as follows:
start.select_difficulty(2)Module Search Path
The user has to ensure that when he finds the module, he needs to do one of the following:
- Put mod.py in the directory where the input script is located, or the current directory if interactive
- Modify the PYTHONPATH environment variable to contain the directory where mod.py is located before starting the interpreter. Or put mod.py in one of the directories already contained in the PYTHON PATH variable.
- Put mod.py in one of the installation-dependent directories, which you may or may not have write-access to, depending on the OS.